I – Basics of DevOps
January 28, 2022

In the year 2008, the concept of DevOps raised out as a result of a discussion between Patrick Debois and Andrew Clay, project manager, a Belgian consultant, and agile practitioner.
DevOps is a set of tools, Cultural Philosophies and practices, designed to shorten the software development life-cycle process. DevOps signify a change in IT culture, focusing on quick IT service delivery through the adoption of lean, agile practices in the context of a system-oriented method. By adopting a DevOps culture into business along with DevOps Practice and tools, teams gain the ability to better respond to customer needs and increase the confidence in the apps they develop and achieve business goals quicker.

Benefits of DevOps

DevOps Vs. Traditional Approach
| DevOps | Traditional |
|
|
DevOps Tools
To implement DevOps and work within the DevOps life cycle, following tools required
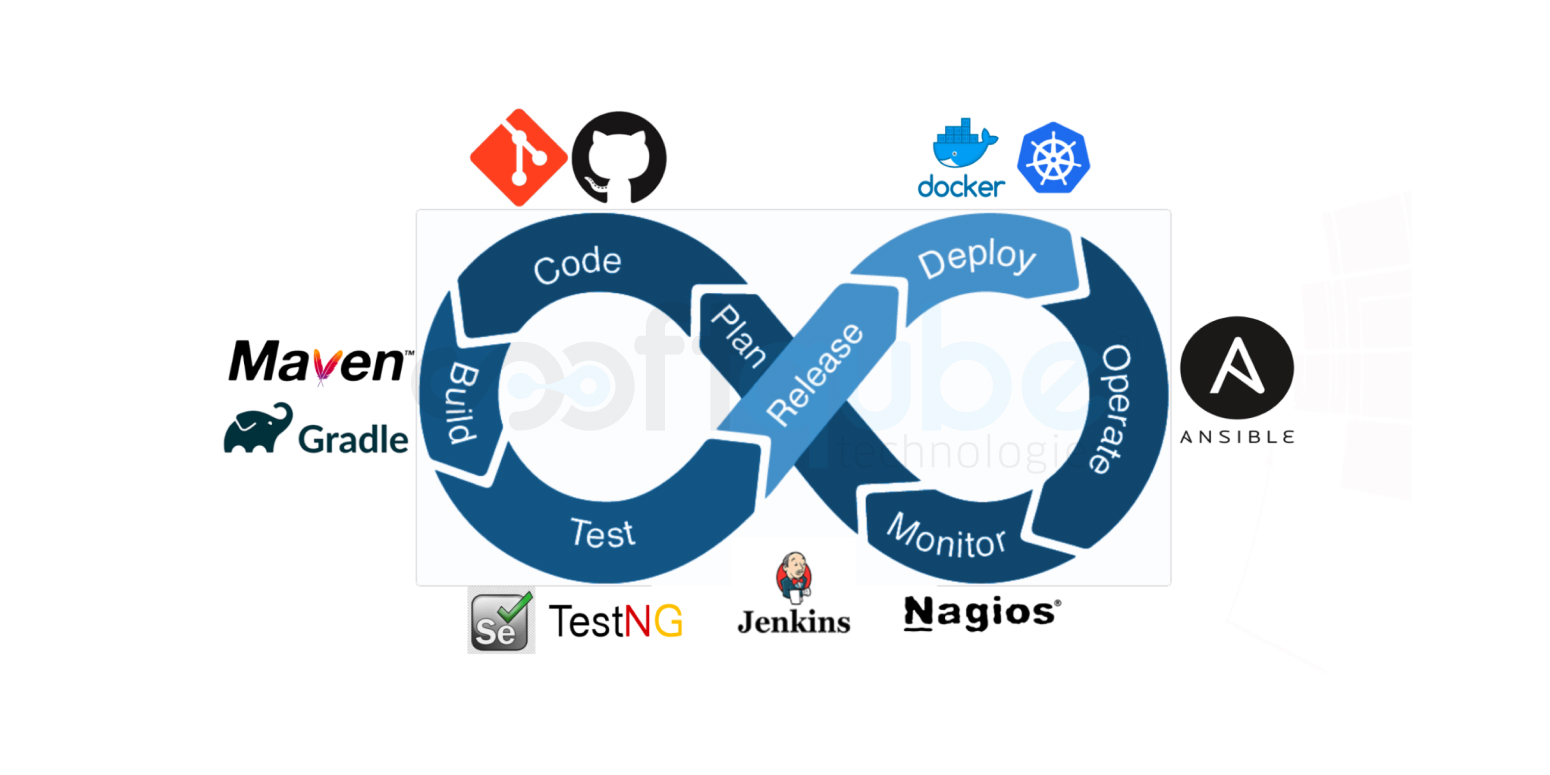
- Code:For Source-Code Management (SCM) ,version control tools such as Git,GitHub, Subversion, TFS, and Mercurial are used.
- Build: For automating the build process of an executable application from source code, software build tools such as Maven, Gradle, Ant, and Grunt are used.
- In the continuous testing phase, the built software is continuously tested for bugs using testing tools such as Selenium, TestNG, and JUnit.
- Release: CI/CD pipelines are created for procuring updated source code and constructing the build into .exeformat using tools such as Jenkins.
- Operate:For deployment and operations phase, CMT and automation tools such as Jenkins, AWS CodeDeploy, Chef, Puppet, Ansible, and Terraform are used.
- Monitor:For monitoring system performance and productivity, to reduce (or even eliminate) downtime, monitoring tools such as Nagios are used.
- Deploy: For packaging an application with its required libraries, frameworks, and configuration files to efficiently run it in various computing environments, containerization tools such as Docker and Kubernetes are used.
Key Takeaways
- DevOps is a set of practices and tools designed to shorten the life cycle of a software development process
- Networking and cost-related issues, tools and software compatibility, and DevOps culture are a few challenges in traditional SDLC approach
- Agile is an iterative development procedure that promotes constant iteration of development and testing all over the life cycle of a project.
- Saas, PaaS, and IaaS are the three models of cloud computing services which help to implement DevOps in the cloud.
- Continuous development, continuous testing, continuous integration, continuous deployment, and continuous monitoring are the five phases of DevOps.








